Microservice Discovery Integration
FSM, as a service mesh product, operates on the concept of a “unified service directory” to manage and accommodate various microservice architectures. It automatically identifies and integrates deployed services into a centralized service directory. This enables real-time and automated interactions among microservices, whether they are deployed on Kubernetes (K8s) or other environments.
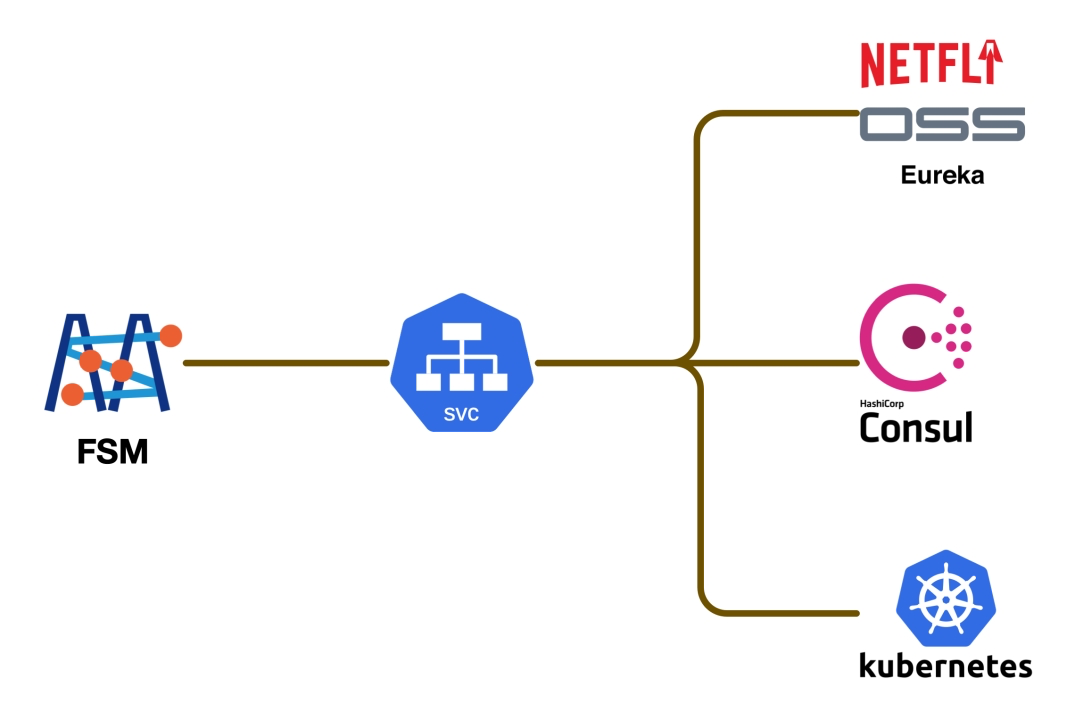
For non-K8s environments, FSM supports multiple popular service registries. This means it can integrate with different service discovery systems, including:
- Consul: A service mesh solution by HashiCorp for service discovery and configuration.
- Eureka: A service discovery tool developed by Netflix, part of the Spring Cloud Netflix microservice suite.
- Nacos: An open-source service discovery and configuration management system by Alibaba, aimed at providing dynamic service discovery and configuration management for cloud-native applications.
Adapting these registries, FSM enhances its application in hybrid architectures, allowing users to enjoy the benefits of a service mesh without being limited to a specific microservice framework. This compatibility positions FSM as a strong service mesh option in diverse microservice environments.
Unified Service Directory
The unified service directory provides a smooth integration experience. By abstracting services from different microservice registries into Kubernetes services (K8s Services), FSM standardizes service information. This approach has several key advantages:
- Simplified service discovery: Services from different sources need not write and maintain multiple sets of code for different discovery mechanisms; everything is uniformly handled through K8s Services.
- Reduced complexity: Encapsulating different service registries as K8s Services means users only need to interact with the K8s API, simplifying operations.
- Seamless cloud-native integration: For services already running on Kubernetes, this unified service model integrates seamlessly, enhancing inter-service operability.
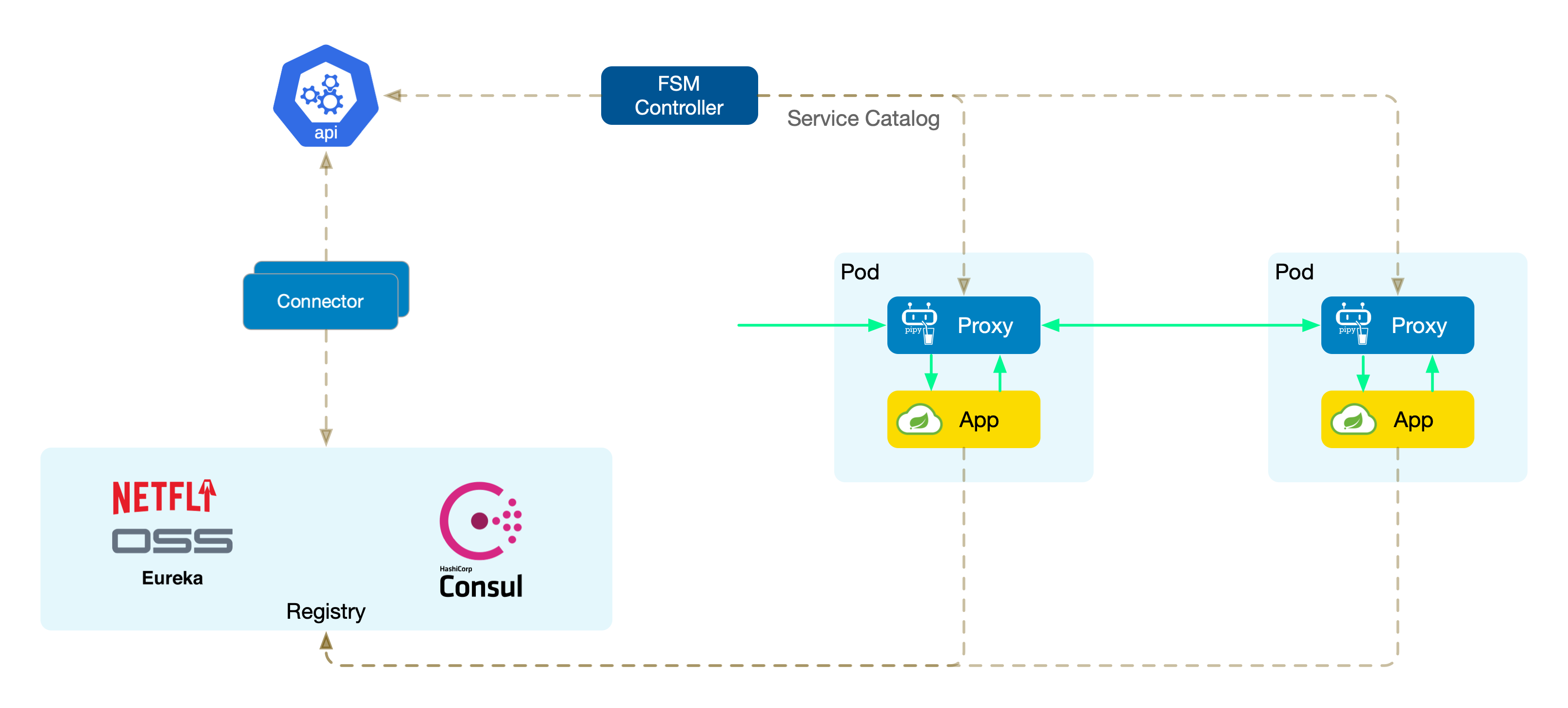
Connectors
FSM uses framework-specific connectors to interface with different microservice registries. Each connector is tasked with communicating with a specific registry (such as Consul, Eureka, or Nacos), performing key tasks like service registration, monitoring service changes, encapsulating as K8s Services, and writing to the cluster.
Connectors are independent components developed in Go (theoretically supporting other languages as well) that can quickly interface with packages provided by the corresponding registry.
Next, we demonstrate integrating Spring Cloud Consul microservices into the service mesh and testing the commonly used canary release scenario.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.