Identity and Access Management
In this demonstration, we will extend the IAM (Identity and Access Management) feature for the service mesh to enhance the security of the service. When service A accesses service B, it will carry the obtained token. After receiving the request, service B verifies the token through the authentication service, and based on the verification result, decides whether to serve the request or not.
Two plugins are required here:
token-injectorto inject the token into the request from service Atoken-verifyerto verify the identity of the request accessing service B.
Both of them handle outbound and inbound traffic, respectively.
Corresponding to this are two PluginChains:
token-injector-chaintoken-verifier-chain
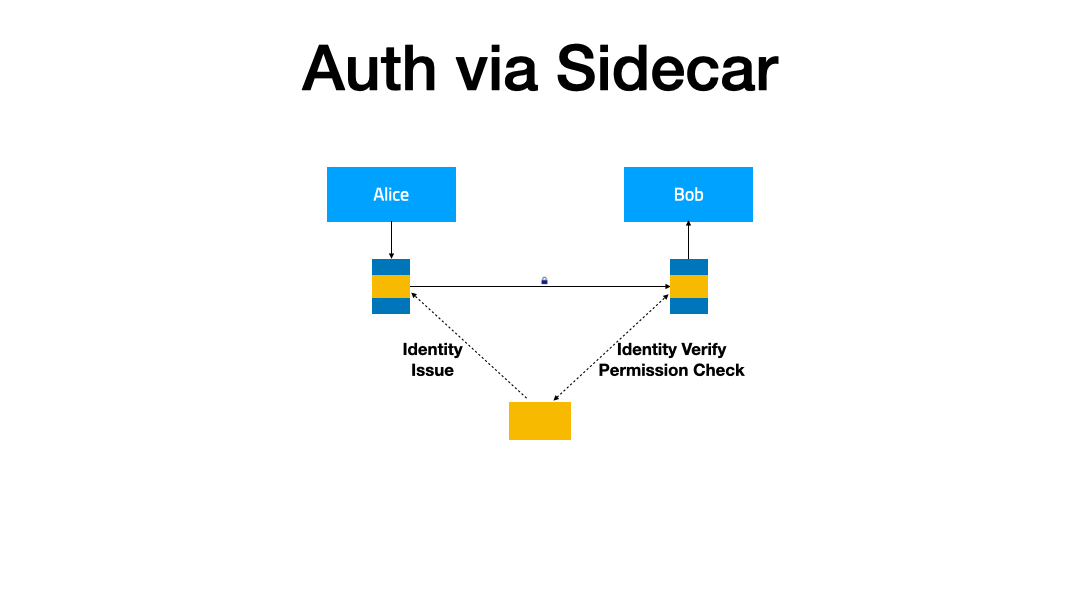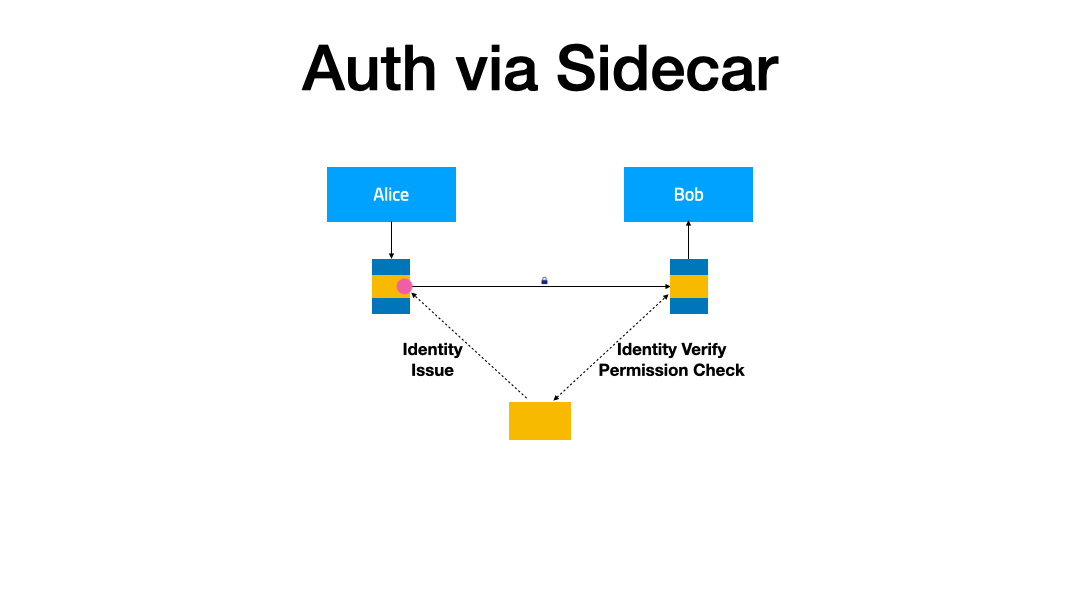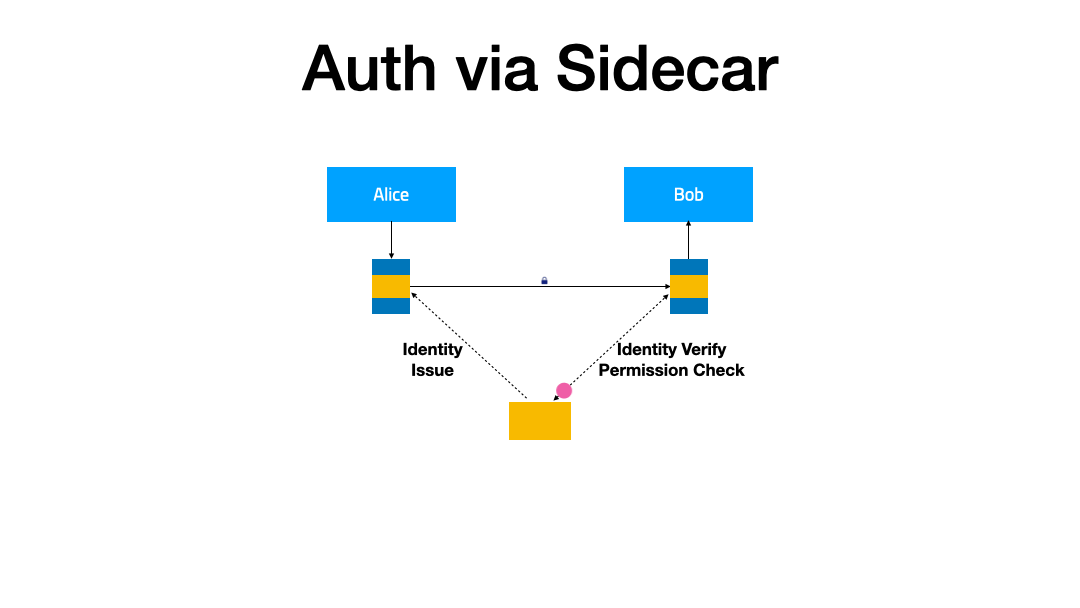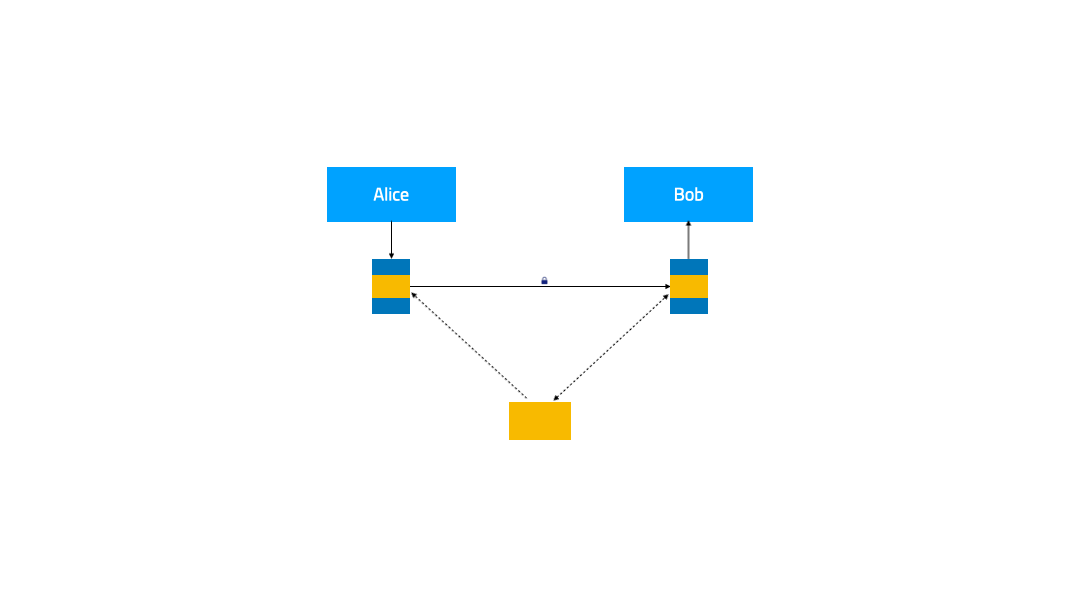
Prerequisites
- Kubernetes cluster running Kubernetes v1.19.0 or greater.
- Have fsm installed.
- Have
kubectlavailable to interact with the API server. - Have
fsmCLI available for managing the service mesh. - Have
jqcommand available.
Deploy demo services
kubectl create namespace curl
fsm namespace add curl
kubectl apply -n curl -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/flomesh-io/fsm-docs/main/manifests/samples/curl/curl.yaml
kubectl create namespace httpbin
fsm namespace add httpbin
kubectl apply -n httpbin -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/flomesh-io/fsm-docs/main/manifests/samples/httpbin/httpbin.yaml
sleep 2
kubectl wait --for=condition=ready pod -n curl -l app=curl --timeout=90s
kubectl wait --for=condition=ready pod -n httpbin -l app=httpbin --timeout=90s
curl_pod=`kubectl get pod -n curl -l app=curl -o jsonpath='{.items..metadata.name}'`
httpbin_pod=`kubectl get pod -n httpbin -l app=httpbin -o jsonpath='{.items..metadata.name}'`
To view the content of the plugin chains for both services. The built-in plugins are located in the modules directory.
These built-in plugins are native functions provided by the service mesh and are not configured through plugin mechanism, but can be overridden via
pluginmechanism.
fsm proxy get config_dump -n curl $curl_pod | jq '.Chains."outbound-http"'
[
"modules/outbound-http-routing.js",
"modules/outbound-metrics-http.js",
"modules/outbound-tracing-http.js",
"modules/outbound-logging-http.js",
"modules/outbound-circuit-breaker.js",
"modules/outbound-http-load-balancing.js",
"modules/outbound-http-default.js"
]
fsm proxy get config_dump -n httpbin $httpbin_pod | jq '.Chains."inbound-http"'
[
"modules/inbound-tls-termination.js",
"modules/inbound-http-routing.js",
"modules/inbound-metrics-http.js",
"modules/inbound-tracing-http.js",
"modules/inbound-logging-http.js",
"modules/inbound-throttle-service.js",
"modules/inbound-throttle-route.js",
"modules/inbound-http-load-balancing.js",
"modules/inbound-http-default.js"
]
Test communication between the applications.
kubectl exec $curl_pod -n curl -c curl -- curl -Is http://httpbin.httpbin:14001/get
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
server: gunicorn/19.9.0
date: Sun, 05 Feb 2023 05:42:51 GMT
content-type: application/json
content-length: 304
access-control-allow-origin: *
access-control-allow-credentials: true
connection: keep-alive
Deploy authentication service
Deploy a standalone authentication service to authenticate requests and return 200 or 401. For simplicity, here we have hard-coded a valid token as 2f1acc6c3a606b082e5eef5e54414ffb
kubectl create namespace auth
kubectl apply -n auth -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: ext-auth
name: ext-auth
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: ext-auth
strategy: {}
template:
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
app: ext-auth
spec:
containers:
- command:
- pipy
- -e
- |2-
pipy({
_acceptTokens: ['2f1acc6c3a606b082e5eef5e54414ffb'],
_allow: false,
})
// Pipeline layouts go here, e.g.:
.listen(8079)
.demuxHTTP().to($ => $
.handleMessageStart(
msg => ((token = msg?.head?.headers?.['x-iam-token']) =>
_allow = token && _acceptTokens?.find(el => el == token)
)()
)
.branch(() => _allow, $ => $.replaceMessage(new Message({ status: 200 })),
$ => $.replaceMessage(new Message({ status: 401 }))
)
)
image: flomesh/pipy:latest
name: pipy
resources: {}
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: ext-auth
name: ext-auth
spec:
ports:
- port: 8079
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8079
selector:
app: ext-auth
EOF
Enable plugin policy mode
To enable plugin policy, the mesh configuration needs to be modified as plugin policies are not enabled by default.
export fsm_namespace=fsm-system
kubectl patch meshconfig fsm-mesh-config -n "$fsm_namespace" -p '{"spec":{"featureFlags":{"enablePluginPolicy":true}}}' --type=merge
Declaring a plugin
Plugin token-injector:
metadata.name: the name of the plugin, which is also the name of the plugin script. For example, this plugin will be saved astoken-injector.jsstored in the plugins directory of the code repository.spec.pipyscript: the PipyJS script content, which is the functional logic code, stored in the script fileplugins/token-injector.js. Context metadata that is built-in to the system can be used within the script.spec.priority: the priority of the plugin, with optional values of 0-65535. The higher the value, the higher the priority, and the earlier the plugin is positioned in the plugin chain. The value here is115, which, based on the built-in plugin list in Helm values.yaml, will be positioned betweenmodules/outbound-circuit-breaker.jsandmodules/outbound-http-load-balancing.js, executed after the circuit breaker logic is processed and before the load balancer forwards to the upstream.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
kind: Plugin
apiVersion: plugin.flomesh.io/v1alpha1
metadata:
name: token-injector
spec:
priority: 115
pipyscript: |+
(
pipy({
_pluginName: '',
_pluginConfig: null,
_accessToken: null,
})
.import({
__service: 'outbound-http-routing',
})
.pipeline()
.onStart(
() => void (
_pluginName = __filename.slice(9, -3),
_pluginConfig = __service?.Plugins?.[_pluginName],
_accessToken = _pluginConfig?.AccessToken
)
)
.handleMessageStart(
msg => _accessToken && (msg.head.headers['x-iam-token'] = _accessToken)
)
.chain()
)
EOF
Plugin token-verifier
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
kind: Plugin
apiVersion: plugin.flomesh.io/v1alpha1
metadata:
name: token-verifier
spec:
priority: 115
pipyscript: |+
(
pipy({
_pluginName: '',
_pluginConfig: null,
_verifier: null,
_authPaths: null,
_authRequred: false,
_authSuccess: undefined,
})
.import({
__service: 'inbound-http-routing',
})
.pipeline()
.onStart(
() => void (
_pluginName = __filename.slice(9, -3),
_pluginConfig = __service?.Plugins?.[_pluginName],
_verifier = _pluginConfig?.Verifier,
_authPaths = _pluginConfig?.Paths && _pluginConfig.Paths?.length > 0 && (
new algo.URLRouter(Object.fromEntries(_pluginConfig.Paths.map(path => [path, true])))
)
)
)
.handleMessageStart(
msg => _authRequred = (_verifier && _authPaths?.find(msg.head.headers.host, msg.head.path))
)
.branch(
() => _authRequred, (
$ => $
.fork().to($ => $
.muxHTTP().to($ => $.connect(()=> _verifier))
.handleMessageStart(
msg => _authSuccess = (msg.head.status == 200)
)
)
.wait(() => _authSuccess !== undefined)
.branch(() => _authSuccess, $ => $.chain(),
$ => $.replaceMessage(
() => new Message({ status: 401 }, 'Unauthorized!')
)
)
),
$ => $.chain()
)
)
EOF
Setting up plugin-chain
plugin chain token-injector-chain:
metadata.name: name of plugin chain resourcetoken-injector-chainspec.chainsname: name of the plugin chain, one of the 4 plugin chains, here it is outbound-http which is the HTTP protocol processing stage for outbound traffic.plugins: list of plugins to be inserted into the plugin chain, heretoken-injectoris inserted into the plugin chain.
spec.selectors: target of the plugin chain, using Kubernetes label selector scheme.podSelector: pod selector, selects pods with labelapp=curl.namespaceSelector: namespace selector, selects namespaces managed by the mesh, i.e.,flomesh.io/monitored-by=fsm.
kubectl apply -n curl -f - <<EOF
kind: PluginChain
apiVersion: plugin.flomesh.io/v1alpha1
metadata:
name: token-injector-chain
spec:
chains:
- name: outbound-http
plugins:
- token-injector
selectors:
podSelector:
matchLabels:
app: curl
matchExpressions:
- key: app
operator: In
values: ["curl"]
namespaceSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: flomesh.io/monitored-by
operator: In
values: ["fsm"]
EOF
plugin chain token-verifier-chain:
kubectl apply -n httpbin -f - <<EOF
kind: PluginChain
apiVersion: plugin.flomesh.io/v1alpha1
metadata:
name: token-verifier-chain
spec:
chains:
- name: inbound-http
plugins:
- token-verifier
selectors:
podSelector:
matchLabels:
app: httpbin
namespaceSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: flomesh.io/monitored-by
operator: In
values: ["fsm"]
EOF
After applying the plugin chain configuration, the plugin chains of the two applications can be viewed now. From the results, we can see the two plugins located in the plugins directory. Our declared plugins have been configured in the two applications through the configuration of the plugin chain.
fsm proxy get config_dump -n curl $curl_pod | jq '.Chains."outbound-http"'
[
"modules/outbound-http-routing.js",
"modules/outbound-metrics-http.js",
"modules/outbound-tracing-http.js",
"modules/outbound-logging-http.js",
"modules/outbound-circuit-breaker.js",
"plugins/token-injector.js",
"modules/outbound-http-load-balancing.js",
"modules/outbound-http-default.js"
]
fsm proxy get config_dump -n httpbin $httpbin_pod | jq '.Chains."inbound-http"'
[
"modules/inbound-tls-termination.js",
"modules/inbound-http-routing.js",
"modules/inbound-metrics-http.js",
"modules/inbound-tracing-http.js",
"modules/inbound-logging-http.js",
"modules/inbound-throttle-service.js",
"modules/inbound-throttle-route.js",
"plugins/token-verifier.js",
"modules/inbound-http-load-balancing.js",
"modules/inbound-http-default.js"
]
After applying the plugin configuration, but we haven’t yet make changes to plugin configuration, the application curl can still access httpbin.
kubectl exec $curl_pod -n curl -c curl -- curl -Is http://httpbin.httpbin:14001/get
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
server: gunicorn/19.9.0
date: Sun, 05 Feb 2023 06:34:33 GMT
content-type: application/json
content-length: 304
access-control-allow-origin: *
access-control-allow-credentials: true
connection: keep-alive
Setting up plugin configuration
We will first apply the configuration of the plugin token-verifier. Here, the authentication service ext-auth.auth:8079 and the request /get that needs to be authenticated are configured.
spec.configcontains the contents of the plugin configuration, which will be converted to JSON format. For example, the configuration applied to thetoken-verifierplugin exists in the following JSON form:{ "Plugins": { "token-verifier": { "Paths": [ "/get" ], "Verifier": "ext-auth.auth:8079" } } }
kubectl apply -n httpbin -f - <<EOF
kind: PluginConfig
apiVersion: plugin.flomesh.io/v1alpha1
metadata:
name: token-verifier-config
spec:
config:
Verifier: 'ext-auth.auth:8079'
Paths:
- "/get"
plugin: token-verifier
destinationRefs:
- kind: Service
name: httpbin
namespace: httpbin
EOF
At this time, the application curl cannot access the httbin /get path because a access token has not been configured for curl yet.
kubectl exec $curl_pod -n curl -c curl -- curl -Is http://httpbin.httpbin:14001/get
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
content-length: 13
connection: keep-alive
But accessing /headers path doesn’t require any authentication.
kubectl exec $curl_pod -n curl -c curl -- curl -Is http://httpbin.httpbin:14001/headers
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
server: gunicorn/19.9.0
date: Sun, 05 Feb 2023 06:37:05 GMT
content-type: application/json
content-length: 217
access-control-allow-origin: *
access-control-allow-credentials: true
connection: keep-alive
Next, the configuration of the plugin token-injector is applied to configure the access token 2f1acc6c3a606b082e5eef5e54414ffb for the application’s requests. This token is also a valid token hardcoded in the authentication service.
kubectl apply -n curl -f - <<EOF
kind: PluginConfig
apiVersion: plugin.flomesh.io/v1alpha1
metadata:
name: token-injector-config
spec:
config:
AccessToken: '2f1acc6c3a606b082e5eef5e54414ffb'
plugin: token-injector
destinationRefs:
- kind: Service
name: httpbin
namespace: httpbin
EOF
After applying the configuration for the token-injector plugin, the requests from the curl application will now have the access token 2f1acc6c3a606b082e5eef5e54414ffb configured. As a result, when accessing the /get path of httpbin, the requests will pass authentication and be accepted by httpbin.
kubectl exec $curl_pod -n curl -c curl -- curl -Is http://httpbin.httpbin:14001/get
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
server: gunicorn/19.9.0
date: Sun, 05 Feb 2023 06:39:54 GMT
content-type: application/json
content-length: 360
access-control-allow-origin: *
access-control-allow-credentials: true
connection: keep-alive
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.